In today's digital world, data is a valuable asset. Protecting this data is crucial for businesses and individuals alike.
Data fiduciaries play a key role in safeguarding personal information. They are responsible for managing and protecting data on behalf of others.
Understanding the role of data fiduciaries is essential for compliance with data protection laws. This is especially true in India, where the DPDP Act governs data practices.
The DPDP Act outlines specific responsibilities for data fiduciaries. It also defines criteria for identifying significant data fiduciaries.
Compliance with these regulations is not just a legal obligation. It is also vital for maintaining consumer trust and ensuring data security.
This article will explore the meaning and responsibilities of data fiduciaries. We will also discuss the implications of the DPDP Act for businesses in India.
Data Fiduciary Meaning: Definition and Context
At its core, a data fiduciary is an entity entrusted with the responsibility of handling data. This role involves managing and safeguarding personal data on behalf of individuals.
The term "data fiduciary" implies a relationship of trust between the data holder and the data principal, the individual whose data is collected.
In the context of data protection, a data fiduciary is expected to act in the best interests of the data principal. This includes ensuring data security and privacy.
A data fiduciary can take various forms:
• Businesses collecting customer data
• Online platforms managing user information
• Service providers accessing client details
In India, the DPDP Act provides the legal framework for data fiduciaries. It sets out the standards for how personal data should be processed.
Understanding the meaning of a data fiduciary is essential for any entity handling data. This comprehension helps align business practices with legal obligations.
By recognizing their role, data fiduciaries can implement effective data protection measures. This not only ensures compliance but also builds consumer trust.
The evolving landscape of digital privacy emphasizes the importance of data fiduciaries. As stewards of personal data, they play a crucial part in today's information-driven economy.
The DPDP Act: Overview and Relevance to Data Fiduciaries in India
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act is a vital piece of legislation in India. It was designed to safeguard personal data and strengthen privacy rights. This law is crucial for data fiduciaries.
The DPDP Act outlines responsibilities for entities handling data, ensuring that personal information is protected. It sets out requirements for processing, storing, and transferring data. This helps maintain a high standard of privacy.
Key components of the DPDP Act relevant to data fiduciaries include:
• Obligations to process data lawfully and transparently
• Requirements for securing personal data against unauthorized access
• Protocols for data breach notifications
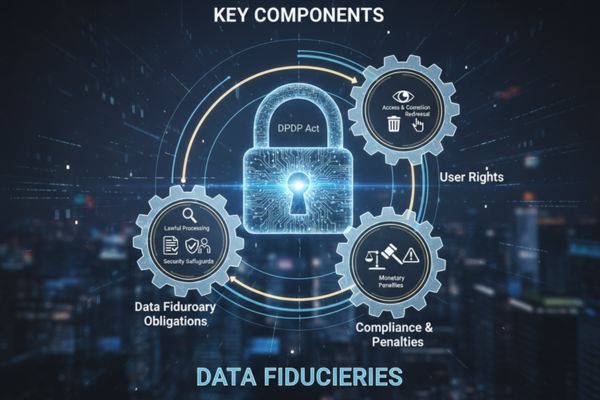
The Act defines the rules for Significant Data Fiduciaries. These are entities with a large-scale impact on privacy. They must adhere to additional compliance measures.
By establishing clear guidelines, the DPDP Act serves as a blueprint. It helps data fiduciaries understand their responsibilities. They must ensure the secure handling and processing of personal data.
Understanding the DPDP Act is essential for data fiduciaries operating in India. It lays the foundation for compliant data management practices and enhanced consumer protection.
In a digital economy, such legal frameworks are paramount. They provide trust and transparency in data handling processes.
Significant Data Fiduciary under DPDP Act: Criteria and Identification
A Significant Data Fiduciary (SDF) is a crucial designation under the DPDP Act. This classification impacts entities with a substantial role in data processing and privacy.
To qualify as a Significant Data Fiduciary, certain criteria must be met. These include the volume of data processed and the data's sensitivity. Both are critical factors for determining this status.
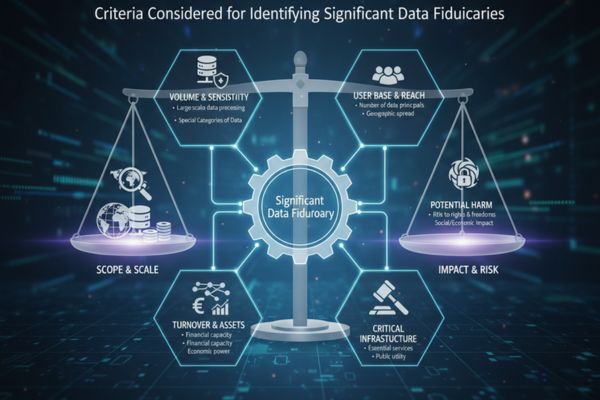
Here are some criteria considered for identifying SDFs:
• Volume and nature of personal data processed
• Sensitivity of the data being handled
• Impact on data principals, particularly concerning rights and freedoms
• Potential for harm if data is compromised
Significant Data Fiduciaries have additional responsibilities. They must implement enhanced security measures and more stringent compliance protocols. This ensures better protection of personal data.
The government or regulatory body assigns the SDF status. It assesses the nature of operations and potential risks involved in data processing activities. This is vital for maintaining strict data protection standards.
Entities recognized as SDFs are often larger organizations. These might include tech giants, financial institutions, or health services. Their role in handling vast amounts of sensitive information makes them pivotal players in data protection.
By identifying SDFs, the DPDP Act targets those with significant data processing impacts. This ensures greater responsibility and accountability, enhancing overall data protection efforts in India. As a result, the trust in digital interactions grows, fostering a safer environment for data principals.
Obligations of Significant Data Fiduciary: Key Responsibilities
The role of a Significant Data Fiduciary (SDF) carries critical responsibilities. These obligations aim to safeguard personal data and uphold privacy standards.
SDFs must implement stringent security measures. This includes using advanced encryption and secure data storage solutions. These actions help protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Compliance with the DPDP Act is mandatory for SDFs. They need to adopt data protection and privacy policies aligned with the law. Regular audits and assessments ensure ongoing compliance.
Key obligations include:
• Conducting data protection impact assessments
• Training employees on data security and privacy practices
• Appointing a Data Protection Officer to oversee data governance

SDFs must maintain transparency with data principals. Providing clear, accessible privacy notices detailing data use is essential. This builds trust and informs individuals about their data rights.
Reporting data breaches promptly is another crucial responsibility. Quick action can mitigate potential harm and demonstrates accountability. This ensures that affected individuals are informed without delay.
Another obligation involves cross-border data transfers. SDFs should ensure that international data sharing meets legal and privacy standards. This includes obtaining necessary consents and implementing safeguard measures.
Further obligations consist of:
• Regularly updating data protection protocols
• Monitoring and analyzing data processing activities
• Ensuring fair and lawful data handling practices
Meeting these responsibilities is not just a legal requirement but a moral one. It secures the data landscape for all users, enhancing overall trust in digital operations.
By fulfilling these obligations, SDFs contribute to a robust data protection ecosystem. This, in turn, strengthens consumer confidence in digital services. The success of data protection frameworks hinges on diligent compliance by these key players. Their role underscores the importance of responsible data stewardship in today's interconnected world.
DPDP Act Compliance for Significant Data Fiduciaries: Steps and Best Practices
Achieving compliance with the DPDP Act is crucial for Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs). This ensures they effectively manage personal data and protect privacy rights.
The first step is to perform a comprehensive data audit. This identifies the types of data collected and processed. Understanding data flows is essential in designing a robust compliance strategy.
SDFs should also assess their current data protection practices. This evaluation helps pinpoint areas needing improvement. Implementing necessary changes can ensure adherence to DPDP Act requirements.
To facilitate compliance, consider these best practices:
• Develop a detailed data protection policy
• Regularly conduct employee training sessions on privacy laws

Deploying advanced technology solutions can enhance data security. Encryption, access controls, and secure data handling are vital components. These technologies protect against potential threats and breaches.
Further, maintaining transparent communication with data principals is essential. Clearly articulate how personal data is used and shared. Transparency fosters trust and aligns with legal obligations.
Regular monitoring and assessments form an integral part of compliance. Establish mechanisms for continuous oversight and evaluation. This proactive approach helps detect and address any compliance gaps.
Additional practices include:
• Setting up efficient data breach response protocols
• Conducting regular updates of security measures
By adopting these steps and best practices, SDFs can achieve and maintain compliance with the DPDP Act. This not only adheres to legal requirements but also builds a foundation of trust with their stakeholders. Compliance ensures data principals feel confident that their data is managed responsibly. It strengthens the overall integrity of the digital environment in which these fiduciaries operate.
Data Fiduciary Responsibilities in India: Practical Implications
Data fiduciaries in India hold critical responsibilities. These responsibilities ensure personal data is handled with care and integrity.
One primary obligation is transparency. Fiduciaries must provide clear information to data principals. They should explain data collection purposes, usage, and sharing practices.
Another responsibility is data protection. Implementing robust security measures is essential. This includes safeguarding data against unauthorized access and breaches.

Additionally, data fiduciaries need to respect consent. Obtaining explicit permission from data principals before processing their data is crucial. Any changes in data processing should involve updated consent procedures.
The impacts of these responsibilities are far-reaching. They help build trust with customers and partners. Ethical data management practices can enhance brand reputation.
Key responsibilities include:
• Ensuring data accuracy and reliability
• Establishing mechanisms for data correction or deletion
• Regularly reviewing data protection policies
For fiduciaries, meeting these obligations requires ongoing effort. Staying informed about regulatory changes and updates is vital. They must adapt their practices accordingly to remain compliant.
Consequences of non-compliance can be severe. Legal penalties and reputational damage may follow any breach. Therefore, maintaining high standards in data handling is both a legal and strategic necessity.
Ultimately, the role of data fiduciaries shapes the digital landscape. They influence how data privacy and security are perceived and enforced across India.
Data Fiduciary vs. Data Controller: Global Comparisons
Data fiduciaries and data controllers share similar roles but differ in context and terminology across jurisdictions. While fiduciaries are recognized in India, controllers are prevalent in Europe under the GDPR framework.
A data controller defines how and why personal data is processed. In contrast, a data fiduciary safeguards data principals' interests. Fiduciaries have ethical obligations to the data subjects.

Despite differences, both entities focus on data protection. Here's a quick comparison:
• Region-Specific Names: Controllers (EU) vs. Fiduciaries (India)
• Core Function: Decide processing purpose vs. Protect subjects' interests
• Legal Framework: GDPR in EU vs. DPDP Act in India
Globally, these roles reflect similar responsibilities. Both require consent management, data security, and regulatory compliance. Their goal is to foster trust and protect privacy.
International trends influence these roles. Data privacy laws are increasingly mirroring each other. As technology evolves, aligning global practices could simplify cross-border data transfers.
Recognizing these similarities helps organizations operate internationally. A deeper understanding aids compliance with varying legal systems, ensuring efficient data handling worldwide.
Challenges and Opportunities for Data Fiduciaries
Data fiduciaries face numerous challenges in executing their roles effectively. The vast amount of data generated daily complicates data management. Ensuring data accuracy while maintaining security is a daunting task for fiduciaries.
Adapting to constantly evolving regulations is another significant challenge. Laws like the DPDP Act are complex and require ongoing updates to compliance strategies. Fiduciaries must stay informed of any legislative changes.
Despite these challenges, opportunities abound for data fiduciaries. Leveraging technology can streamline operations and enhance data security. Tools like encryption and AI can improve data management and protection efforts.
Data fiduciaries can also build stronger relationships with data principals. By prioritizing transparency and accountability, fiduciaries can foster trust. Engaging in open communication strengthens these partnerships.
Key considerations for fiduciaries include:
• Staying Updated: Keeping abreast of legal changes
• Embracing Technology: Using advanced tools for data security
• Fostering Trust: Enhancing transparency with data principals
Balancing these challenges and opportunities can transform fiduciary roles. The future offers immense potential for fiduciaries who navigate complexities skillfully. They can pave the way for responsible data practices that benefit all stakeholders.
The Future of Data Fiduciary Responsibilities in India
The future of data fiduciaries in India is evolving rapidly. As digital transformation accelerates, the role of fiduciaries becomes even more critical. Their responsibilities will likely expand with technological advancements.
Data protection regulations in India are poised to become stricter. Future amendments to the DPDP Act may introduce more rigorous compliance requirements. Fiduciaries must prepare to adapt swiftly to these evolving mandates.
Opportunities for innovation will emerge alongside challenges. Implementing cutting-edge technologies can aid fiduciaries in meeting future demands. Cloud services and AI solutions can help manage data more efficiently.
Ultimately, the key to future success lies in adaptability. Data fiduciaries who embrace change will lead the charge in safeguarding data privacy. Their proactive approaches will set benchmarks for others in the industry.
Conclusion: The Importance of Data Fiduciaries in the Digital Age
Data fiduciaries play a crucial role in our interconnected world. They help safeguard sensitive information, ensuring privacy and trust in digital environments. As data usage grows, their importance becomes even more pronounced.
Adhering to the DPDP Act secures consumer confidence and prevents data misuse. Compliance is not just a legal necessity but a way to build a positive reputation. Trust and transparency foster stronger customer relationships.
The responsibility of data fiduciaries extends beyond mere compliance. They must innovate and adapt to technological changes while upholding data ethics. By doing so, they shape a secure digital future, balancing privacy with progress.













